Concurrent User Testing from the Cloud
Concurrent user load testing sends traffic to a web application, web page, or API (Application Programming Interface) to stress the infrastructure. Specific metrics are observed and recorded during the test, and system response times during periods of sustained heavy load are measured. With LoadView, you can increase the number of concurrent users slowly or quickly throughout your test to record how performance is affected under sustained load.
The idea behind concurrent user testing is to identify the response time of a website for a specified number of concurrent users making requests to a website. Concurrent user testing measures how long it takes the server to respond to a specified number of concurrent requests. A concurrent user test is often used to identify bottlenecks in the performance of a website – basically to find out how many concurrent users can make requests of a website until the performance of the site is significantly degraded.
LoadView simulates visitor activity with real browsers controlled by virtual users to replicate various levels of demand on a website or web-based service.
Simultaneous User Testing
Send 10 to 10,000+ simultaneous users to your web application to test the performance of your production hardware, software, and infrastructure. You know there are limits to how much traffic your website can handle, but do you know what those limits are? There are several layers supporting your website that could be a potential bottleneck including web servers, file servers, routers, firewalls, and more. Once you have identified the breaking point, you can then strengthen the weak spots in your system.
Simultaneous user testing is sometimes mistakenly referred to concurrent user testing, however, there is a difference, even if the words themselves indicate that something is happening or occurring at the same time. While concurrent users refer to the number of users using or landing on your website or application at any given time, simultaneous users are users, or visitors, that are carrying out a specific transaction, at the same time, during a specific point in time.
For example, you may have 100 different visitors on a specific page, how does performance compare when 40 users log into your portal at the same time? Or if you operate a hotel, for example, what happens when 100 people try to make a reservation at the same time? These are important factors to understand, as it directly affects the user experience.
Use Case Scenario – Concurrent Load Testing
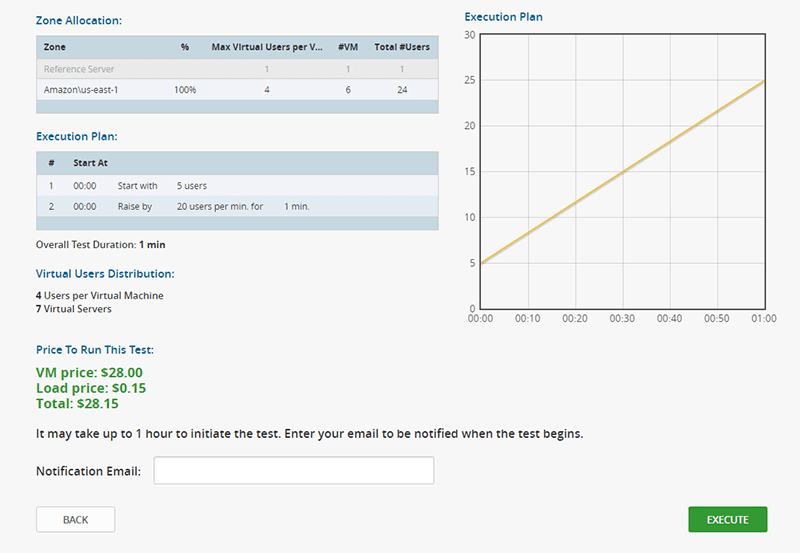
With LoadView, there are a variety of ways you can conduct a concurrent user test. For example, you can begin load testing with as few as 10 concurrent users and run these users for five minutes to establish your baseline performance metrics. After establishing a baseline, you can increase the number of concurrent users by 10 users a minute until you reach 100 concurrent users. You may choose to follow that up with a test run for another five minutes for every 100 additional concurrent users to be sure that the results level out.
Some factors that may cause spikes or drops in web page response time while adding concurrent users include additional allocation of memory on the webs server or additional concurrent database connections on the backend. These could easily cause a spike in the average page load speed while waiting for the system resources to become free only to drop back to normal levels once the resources have been allocated.
To test this, you may choose to run a test of 1,000 to 10,000 concurrent users, or until you feel you have adequately proven that your website is capable of handling peak user numbers. These tests can be used to identify both the volume of users that cause unacceptable page load speeds as well as the number of concurrent page requests that causes the web app to crash. This may be done by running additional load tests that start at a higher volume of users in order to push the system to its limits.